Node:Multi-Dimensional DFTs of Real Data, Next:More DFTs of Real Data, Previous:One-Dimensional DFTs of Real Data, Up:Tutorial
Multi-dimensional DFTs of real data use the following planner routines:
fftw_plan fftw_plan_dft_r2c_2d(int nx, int ny,
double *in, fftw_complex *out,
unsigned flags);
fftw_plan fftw_plan_dft_r2c_3d(int nx, int ny, int nz,
double *in, fftw_complex *out,
unsigned flags);
fftw_plan fftw_plan_dft_r2c(int rank, const int *n,
double *in, fftw_complex *out,
unsigned flags);
as well as the corresponding c2r routines with the input/output
types swapped. These routines work similarly to their complex
analogues, except for the fact that here the complex output array is cut
roughly in half and the real array requires padding for in-place
transforms (as in 1d, above).
As before, n is the logical size of the array, and the
consequences of this on the the format of the complex arrays deserve
careful attention.
Suppose that the real data has dimensions n1 x n2 x n3 x ... x nd
(in row-major order).
Then, after an r2c transform, the output is an n1 x n2 x n3 x ... x (nd/2 + 1)
array of
fftw_complex values in row-major order, corresponding to slightly
over half of the output of the corresponding complex DFT. (The division
is rounded down.) The ordering of the data is otherwise exactly the
same as in the complex-DFT case.
Since the complex data is slightly larger than the real data, some
complications arise for in-place transforms. In this case, the final
dimension of the real data must be padded with extra values to
accommodate the size of the complex data--two values if the last
dimension is even and one if it is odd.
That is, the last dimension of the real data must physically contain
2 * (nd/2+1)
double values (exactly enough to hold the complex data).
This physical array size does not, however, change the logical
array size--only
nd
values are actually stored in the last dimension, and
nd
is the last dimension passed to the plan-creation routine.
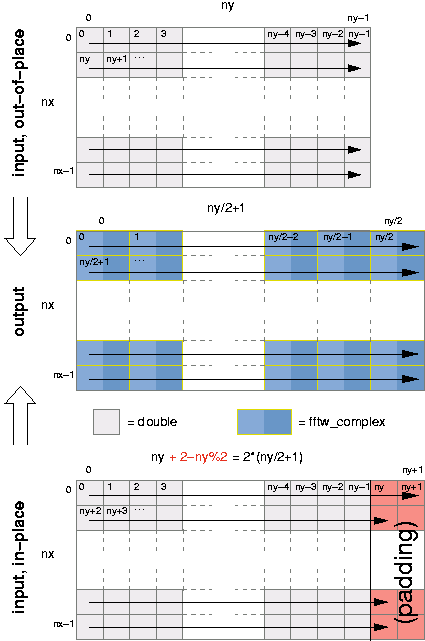
For example, consider the transform of a two-dimensional real array of
size nx by ny. The output of the r2c transform is a
two-dimensional complex array of size nx by ny/2+1, where
the y dimension has been cut nearly in half because of
redundancies in the output. Because fftw_complex is twice the
size of double, the output array is slightly bigger than the
input array. Thus, if we want to compute the transform in place, we
must pad the input array so that it is of size nx by
2*(ny/2+1). If ny is even, then there are two padding
elements at the end of each row (which need not be initialized, as they
are only used for output).
The following illustration depicts the input and output arrays just
described, for both the out-of-place and in-place transforms (with the
arrows indicating consecutive memory locations):

These transforms are unnormalized, so an r2c followed by a c2r transform (or vice versa) will result in the original data scaled by the number of real data elements--that is, the product of the (logical) dimensions of the real data.
(Because the last dimension is treated specially, if it is equal to
1 the transform is not equivalent to a lower-dimensional
r2c/c2r transform. In that case, the last complex dimension also has
size 1 (=1/2+1), and no advantage is gained over the
complex transforms.)